
- DSA 使用 C 教程
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 主页
- 使用 C 语言的 DSA - 概述
- 使用 C 语言的 DSA - 环境
- 使用 C 算法的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 概念
- 使用 C 数组的 DSA
- 使用 C 链表的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 双向链表
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 循环链表
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 堆栈内存溢出
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 解析表达式
- 使用 C 队列的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 优先级队列
- 使用 C 树的 DSA
- 使用 C 哈希表的 DSA
- 使用 C 堆的 DSA
- 使用 C - Graph 的 DSA
- 使用 C 搜索技术的 DSA
- 使用 C 排序技术的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 递归
- 使用 C 语言的 DSA 有用资源
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 快速指南
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 有用资源
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 讨论
使用 C - Graph 的 DSA
概述
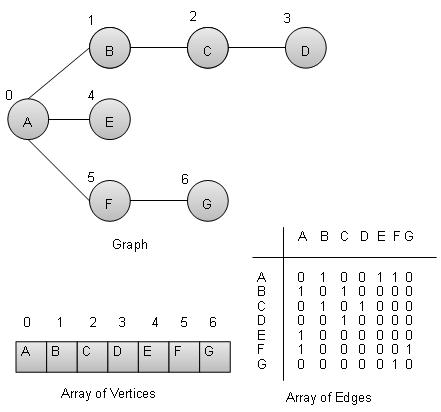
图是一种对数学图进行建模的数据结构。它由一组称为顶点边的连接对组成。我们可以使用顶点数组和边的二维数组来表示图。
重要条款
顶点- 图的每个节点都表示为一个顶点。在下面给出的示例中,标记的圆圈表示顶点。所以A到G是顶点。我们可以使用数组来表示它们,如下图所示。这里A可以通过索引0来标识。B可以通过索引1来标识,依此类推。
Edge - 边表示两个顶点之间的路径或两个顶点之间的线。在下面给出的示例中,从 A 到 B、B 到 C 等的线代表边缘。我们可以使用二维数组来表示数组,如下图所示。这里AB可以在第0行第1列表示为1,BC在第1行第2列表示为1,依此类推,其他组合保持为0。
邻接- 如果两个节点或顶点通过边相互连接,则它们是相邻的。在下面给出的示例中,B 与 A 相邻,C 与 B 相邻,依此类推。
路径- 路径表示两个顶点之间的边序列。在下面给出的示例中,ABCD 表示从 A 到 D 的路径。
基本操作
以下是图的基本主要操作。
添加顶点- 向图中添加一个顶点。
添加边- 在图的两个顶点之间添加边。
显示顶点- 显示图形的顶点。
添加顶点操作
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label){
struct vertex* vertex =
(struct vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
添加边缘操作
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end){
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
显示边缘操作
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex){
printf("%c ",lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label);
}
遍历算法
以下是图上的重要遍历算法。
深度优先搜索- 以深度运动遍历图形。
广度优先搜索- 以广度运动遍历图。
深度优先搜索算法
深度优先搜索算法(DFS)以深度运动方式遍历图,并在任何迭代中出现死端时使用堆栈来记住获取下一个顶点以开始搜索。
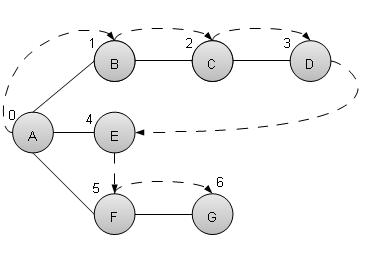
正如上面给出的例子,DFS算法首先从A遍历到B,再到C,再到D,然后到E,然后到F,最后到G。它采用以下规则。
规则 1 - 访问相邻的未访问顶点。标记它已访问过。显示它。将其推入堆栈。
规则 2 - 如果没有找到相邻顶点,则从堆栈中弹出一个顶点。(它将从堆栈中弹出所有没有相邻顶点的顶点。)
规则 3 - 重复规则 1 和规则 2,直到堆栈为空。
void depthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//push vertex index in stack
push(0);
while(!isStackEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at top of the stack
int unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek());
//no adjacent vertex found
if(unvisitedVertex == -1){
pop();
} else {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
push(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//stack is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i < vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
广度优先搜索算法
广度优先搜索算法(BFS)以广度运动方式遍历图,并在任何迭代中出现死端时使用队列来记住获取下一个顶点以开始搜索。
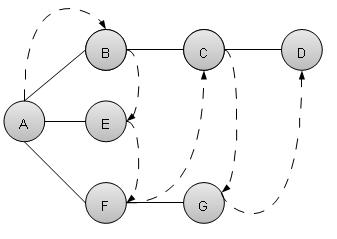
如上面给出的示例,BFS 算法首先从 A 遍历到 B,再到 E,再到 F,然后再遍历到 C,最后遍历到 D。它采用以下规则。
规则 1 - 访问相邻的未访问顶点。标记它已访问过。显示它。将其插入队列中。
规则 2 - 如果没有找到相邻顶点,则从队列中删除第一个顶点。
规则 3 - 重复规则 1 和规则 2,直到队列为空。
void breadthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex=getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1){
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i<vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
例子
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 10
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//stack variables
int stack[MAX];
int top=-1;
//queue variables
int queue[MAX];
int rear=-1;
int front=0;
int queueItemCount = 0;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
struct Vertex* lstVertices[MAX];
//adjacency matrix
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//stack functions
void push(int item) {
stack[++top]=item;
}
int pop() {
return stack[top--];
}
int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
bool isStackEmpty(){
return top == -1;
}
//queue functions
void insert(int data){
queue[++rear] = data;
queueItemCount++;
}
int removeData(){
queueItemCount--;
return queue[front++];
}
bool isQueueEmpty(){
return queueItemCount == 0;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label){
struct Vertex* vertex = (struct Vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct Vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end){
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex){
printf("%c ",lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label);
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex){
int i;
for(i=0; i<vertexCount; i++)
if(adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i]==1 && lstVertices[i]->visited==false)
return i;
return -1;
}
void depthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//push vertex index in stack
push(0);
while(!isStackEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at top of the stack
int unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek());
//no adjacent vertex found
if(unvisitedVertex == -1){
pop();
} else {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
push(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//stack is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i < vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
void breadthFirstSearch(){
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()){
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex=getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1){
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i=0;i<vertexCount;i++){
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
main() {
int i, j;
for(i=0; i<MAX; i++) // set adjacency
for(j=0; j<MAX; j++) // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
addVertex('A'); //0
addVertex('B'); //1
addVertex('C'); //2
addVertex('D'); //3
addVertex('E'); //4
addVertex('F'); //5
addVertex('G'); //6
/* 1 2 3
* 0 |--B--C--D
* A--|
* |
* | 4
* |-----E
* | 5 6
* | |--F--G
* |--|
*/
addEdge(0, 1); //AB
addEdge(1, 2); //BC
addEdge(2, 3); //CD
addEdge(0, 4); //AC
addEdge(0, 5); //AF
addEdge(5, 6); //FG
printf("Depth First Search: ");
//A B C D E F G
depthFirstSearch();
printf("\nBreadth First Search: ");
//A B E F C G D
breadthFirstSearch();
}
如果我们编译并运行上面的程序,那么它将产生以下结果 -
Depth First Search: A B C D E F G Breadth First Search: A B E F C G D