
- DSA 使用 C 教程
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 主页
- 使用 C 语言的 DSA - 概述
- 使用 C 语言的 DSA - 环境
- 使用 C 算法的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 概念
- 使用 C 数组的 DSA
- 使用 C 链表的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 双向链表
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 循环链表
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 堆栈内存溢出
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 解析表达式
- 使用 C 队列的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 优先级队列
- 使用 C 树的 DSA
- 使用 C 哈希表的 DSA
- 使用 C 堆的 DSA
- 使用 C - Graph 的 DSA
- 使用 C 搜索技术的 DSA
- 使用 C 排序技术的 DSA
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 递归
- 使用 C 语言的 DSA 有用资源
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 快速指南
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 有用资源
- 使用 C 的 DSA - 讨论
使用 C 的 DSA - 循环链表
概述
循环链表是链表的一种变体,其中第一个元素指向最后一个元素,最后一个元素指向第一个元素。单链表和双向链表都可以做成循环链表。
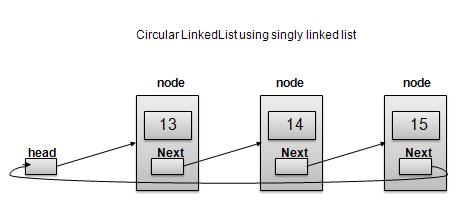
作为循环的单向链表
循环双向链表
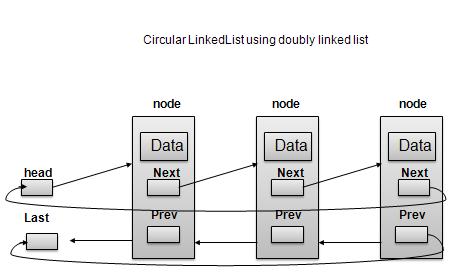
根据上图所示,以下是需要考虑的要点。
在单链表和双链表两种情况下,Last Link'next 都指向列表的第一个链接。
在双向链表的情况下,第一个链接的 prev 指向列表的最后一个。
基本操作
以下是循环列表支持的重要操作。
insert - 在列表的开头插入一个元素。
删除- 从列表的开头插入一个元素。
显示- 显示列表。
长度操作
以下代码演示了基于单链表的循环链表中的插入操作。
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key =key;
link->data=data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
删除操作
下面的代码演示了基于单链表的循环链表中的删除操作。
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head){
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
显示列表操作
以下代码演示了循环链表中的显示列表操作。
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL){
while(ptr->next != ptr){
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
例子
双链表Demo.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
int length(){
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL){
return 0;
}
current = head->next;
while(current != head){
length++;
current = current->next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key =key;
link->data=data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head){
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL){
while(ptr->next != ptr){
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
main() {
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Original List: ");
//print list
printList();
while(!isEmpty()){
struct node *temp = deleteFirst();
printf("\nDeleted value:");
printf("(%d,%d) ",temp->key,temp->data);
}
printf("\nList after deleting all items: ");
printList();
}
输出
如果我们编译并运行上面的程序,那么它将产生以下输出 -
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] Deleted value:(6,56) Deleted value:(5,40) Deleted value:(4,1) Deleted value:(3,30) Deleted value:(2,20) Deleted value:(1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ]