- Spring Boot 教程
- Spring Boot - 主页
- Spring Boot - 简介
- Spring Boot - 快速入门
- Spring Boot - 引导
- Spring Boot - Tomcat 部署
- Spring Boot - 构建系统
- Spring Boot - 代码结构
- Spring Bean 和依赖注入
- Spring Boot - 跑步者
- Spring Boot - 应用程序属性
- Spring Boot - 日志记录
- 构建 RESTful Web 服务
- Spring Boot - 异常处理
- Spring Boot - 拦截器
- Spring Boot - Servlet 过滤器
- Spring Boot - Tomcat 端口号
- Spring Boot - Rest 模板
- Spring Boot - 文件处理
- Spring Boot - 服务组件
- Spring Boot - Thymeleaf
- 使用 RESTful Web 服务
- Spring Boot - CORS 支持
- Spring Boot - 国际化
- Spring Boot - 调度
- Spring Boot - 启用 HTTPS
- Spring Boot-Eureka 服务器
- 向 Eureka 注册服务
- Zuul代理服务器和路由
- Spring Cloud配置服务器
- Spring Cloud 配置客户端
- Spring Boot - 执行器
- Spring Boot - 管理服务器
- Spring Boot - 管理客户端
- Spring Boot - 启用 Swagger2
- Spring Boot - 创建 Docker 镜像
- 追踪微服务日志
- Spring Boot - Flyway 数据库
- Spring Boot - 发送电子邮件
- Spring Boot-Hystrix
- Spring Boot - Web Socket
- Spring Boot - 批量服务
- Spring Boot-Apache Kafka
- Spring Boot - Twilio
- Spring Boot - 单元测试用例
- 休息控制器单元测试
- Spring Boot - 数据库处理
- 保护 Web 应用程序的安全
- Spring Boot - 使用 JWT 的 OAuth2
- Spring Boot - Google 云平台
- Spring Boot - Google OAuth2 登录
- Spring Boot 资源
- Spring Boot - 快速指南
- Spring Boot - 有用的资源
- Spring Boot - 讨论
Spring Boot - 构建 RESTful Web 服务
Spring Boot 为企业应用构建 RESTful Web Services 提供了非常好的支持。本章将详细解释如何使用 Spring Boot 构建 RESTful Web 服务。
注意- 为了构建 RESTful Web 服务,我们需要将 Spring Boot Starter Web 依赖项添加到构建配置文件中。
如果您是 Maven 用户,请使用以下代码在pom.xml文件中添加以下依赖项 -
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency>
如果您是 Gradle 用户,请使用以下代码在build.gradle文件中添加以下依赖项。
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
完整的构建配置文件Maven build – pom.xml的代码如下 -
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns = "http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi = "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation = "http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.tutorialspoint</groupId>
<artifactId>demo</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>demo</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.8.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
完整构建配置文件Gradle Build – build.gradle的代码如下 -
buildscript {
ext {
springBootVersion = '1.5.8.RELEASE'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
}
}
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot'
group = 'com.tutorialspoint'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
testCompile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
}
在继续构建 RESTful Web 服务之前,建议您了解以下注释 -
休息控制器
@RestController 注解用于定义 RESTful Web 服务。它提供 JSON、XML 和自定义响应。其语法如下所示 -
@RestController
public class ProductServiceController {
}
请求映射
@RequestMapping 注释用于定义访问 REST 端点的请求 URI。我们可以定义Request方法来消费和生产对象。默认请求方法为 GET。
@RequestMapping(value = "/products")
public ResponseEntity<Object> getProducts() { }
请求正文
@RequestBody 注解用于定义请求正文内容类型。
public ResponseEntity<Object> createProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
}
路径变量
@PathVariable 注释用于定义自定义或动态请求 URI。请求 URI 中的 Path 变量定义为大括号 {},如下所示 -
public ResponseEntity<Object> updateProduct(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
}
请求参数
@RequestParam注解用于从Request URL中读取请求参数。默认情况下,它是必需参数。我们还可以设置请求参数的默认值,如下所示 -
public ResponseEntity<Object> getProduct(
@RequestParam(value = "name", required = false, defaultValue = "honey") String name) {
}
获取API
默认的 HTTP 请求方法是 GET。此方法不需要任何请求正文。您可以发送请求参数和路径变量来定义自定义或动态 URL。
定义 HTTP GET 请求方法的示例代码如下所示。在这个例子中,我们使用HashMap来存储Product。请注意,我们使用 POJO 类作为要存储的产品。
这里,请求 URI 是/products,它将返回 HashMap 存储库中的产品列表。下面给出了包含 GET 方法 REST Endpoint 的控制器类文件。
package com.tutorialspoint.demo.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.tutorialspoint.demo.model.Product;
@RestController
public class ProductServiceController {
private static Map<String, Product> productRepo = new HashMap<>();
static {
Product honey = new Product();
honey.setId("1");
honey.setName("Honey");
productRepo.put(honey.getId(), honey);
Product almond = new Product();
almond.setId("2");
almond.setName("Almond");
productRepo.put(almond.getId(), almond);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/products")
public ResponseEntity<Object> getProduct() {
return new ResponseEntity<>(productRepo.values(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
发布API
HTTP POST 请求用于创建资源。该方法包含请求正文。我们可以发送请求参数和路径变量来定义自定义或动态 URL。
以下示例显示了定义 HTTP POST 请求方法的示例代码。在这个例子中,我们使用HashMap来存储Product,其中product是一个POJO类。
这里,请求URI是/products,它将产品存储到HashMap存储库后返回String。
package com.tutorialspoint.demo.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.tutorialspoint.demo.model.Product;
@RestController
public class ProductServiceController {
private static Map<String, Product> productRepo = new HashMap<>();
@RequestMapping(value = "/products", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<Object> createProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
productRepo.put(product.getId(), product);
return new ResponseEntity<>("Product is created successfully", HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
}
放置API
HTTP PUT 请求用于更新现有资源。该方法包含一个请求主体。我们可以发送请求参数和路径变量来定义自定义或动态 URL。
下面给出的示例显示了如何定义 HTTP PUT 请求方法。在这个例子中,我们使用HashMap来更新现有的Product,其中product是一个POJO类。
这里的请求 URI 是/products/{id},它将把产品后面的字符串返回到 HashMap 存储库中。请注意,我们使用了 Path 变量{id}来定义需要更新的产品 ID。
package com.tutorialspoint.demo.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.tutorialspoint.demo.model.Product;
@RestController
public class ProductServiceController {
private static Map<String, Product> productRepo = new HashMap<>();
@RequestMapping(value = "/products/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity<Object> updateProduct(@PathVariable("id") String id, @RequestBody Product product) {
productRepo.remove(id);
product.setId(id);
productRepo.put(id, product);
return new ResponseEntity<>("Product is updated successsfully", HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
删除API
HTTP删除请求用于删除现有资源。此方法不包含任何请求正文。我们可以发送请求参数和路径变量来定义自定义或动态 URL。
下面给出的示例显示了如何定义 HTTP DELETE 请求方法。在这个例子中,我们使用HashMap来删除现有的产品,这是一个POJO类。
请求URI是/products/{id},从HashMap存储库中删除产品后它将返回String。我们使用 Path 变量{id}来定义需要删除的产品 ID。
package com.tutorialspoint.demo.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.tutorialspoint.demo.model.Product;
@RestController
public class ProductServiceController {
private static Map<String, Product> productRepo = new HashMap<>();
@RequestMapping(value = "/products/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity<Object> delete(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
productRepo.remove(id);
return new ResponseEntity<>("Product is deleted successsfully", HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
本节为您提供完整的源代码集。请遵守以下代码以了解其各自的功能 -
Spring Boot 主应用程序类 – DemoApplication.java
package com.tutorialspoint.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
POJO 类 – Product.java
package com.tutorialspoint.demo.model;
public class Product {
private String id;
private String name;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
Rest 控制器类 – ProductServiceController.java
package com.tutorialspoint.demo.controller;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.tutorialspoint.demo.model.Product;
@RestController
public class ProductServiceController {
private static Map<String, Product> productRepo = new HashMap<>();
static {
Product honey = new Product();
honey.setId("1");
honey.setName("Honey");
productRepo.put(honey.getId(), honey);
Product almond = new Product();
almond.setId("2");
almond.setName("Almond");
productRepo.put(almond.getId(), almond);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/products/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public ResponseEntity<Object> delete(@PathVariable("id") String id) {
productRepo.remove(id);
return new ResponseEntity<>("Product is deleted successsfully", HttpStatus.OK);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/products/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public ResponseEntity<Object> updateProduct(@PathVariable("id") String id, @RequestBody Product product) {
productRepo.remove(id);
product.setId(id);
productRepo.put(id, product);
return new ResponseEntity<>("Product is updated successsfully", HttpStatus.OK);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/products", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ResponseEntity<Object> createProduct(@RequestBody Product product) {
productRepo.put(product.getId(), product);
return new ResponseEntity<>("Product is created successfully", HttpStatus.CREATED);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/products")
public ResponseEntity<Object> getProduct() {
return new ResponseEntity<>(productRepo.values(), HttpStatus.OK);
}
}
您可以创建一个可执行 JAR 文件,并使用以下 Maven 或 Gradle 命令运行 spring boot 应用程序,如下所示 -
对于 Maven,请使用下面所示的命令 -
mvn clean install
“BUILD SUCCESS”后,您可以在目标目录下找到JAR文件。
对于 Gradle,使用如下所示的命令 -
gradle clean build
“BUILD SUCCESSFUL”后,您可以在build/libs目录下找到JAR文件。
您可以使用下面所示的命令运行 JAR 文件 -
java –jar <JARFILE>
这将在 Tomcat 端口 8080 上启动应用程序,如下所示 -

现在,在 POSTMAN 应用程序中点击下面显示的 URL 并查看输出。
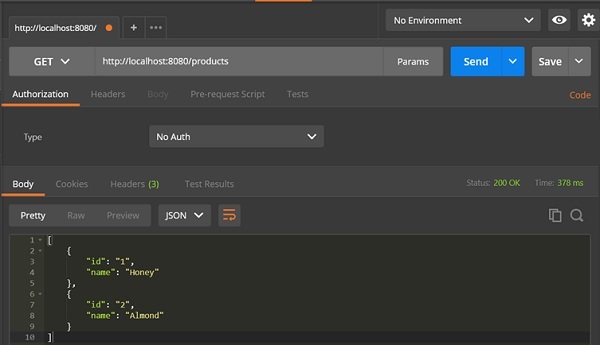
GET API URL 为:http://localhost:8080/products
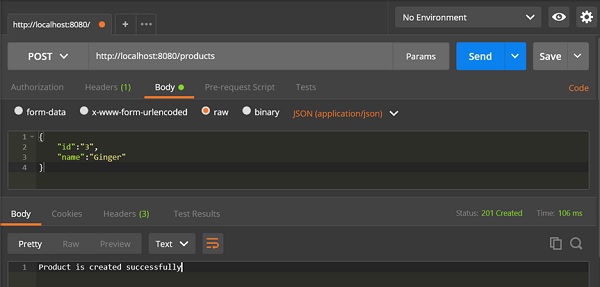
POST API URL 为:http://localhost:8080/products
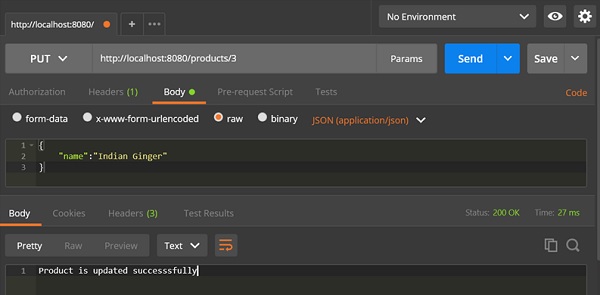
PUT API URL 为:http://localhost:8080/products/3
删除 API URL 为:http://localhost:8080/products/3