
- 算法设计与分析
- 家
- 算法基础知识
- DAA - 简介
- DAA - 算法分析
- DAA-分析方法
- 渐近符号和先验分析
- 时间复杂度
- 马斯特定理
- DAA - 空间复杂性
- 分而治之
- DAA-分而治之
- DAA - 最大最小问题
- DAA-归并排序
- DAA-二分查找
- 施特拉森矩阵乘法
- 唐叶算法
- 河内塔
- 贪心算法
- DAA-贪婪法
- 旅行商问题
- Prim 的最小生成树
- 克鲁斯卡尔的最小生成树
- Dijkstra 的最短路径算法
- 地图着色算法
- DAA-分数背包
- DAA - 带截止日期的作业排序
- DAA - 最佳合并模式
- 动态规划
- DAA-动态规划
- 矩阵链乘法
- 弗洛伊德·沃歇尔算法
- DAA - 0-1 背包
- 最长公共子序列
- 旅行商问题| 动态规划
- 随机算法
- 随机算法
- 随机快速排序
- 卡格的最低削减
- 费舍尔-耶茨洗牌
- 近似算法
- 近似算法
- 顶点覆盖问题
- 设置封面问题
- 旅行推销员近似算法
- 排序技巧
- DAA-快速排序
- DAA-冒泡排序
- DAA——插入排序
- DAA-选择排序
- DAA——希尔排序
- DAA-堆排序
- DAA——桶排序
- DAA——计数排序
- DAA - 基数排序
- 搜索技巧
- 搜索技术介绍
- DAA - 线性搜索
- DAA-二分查找
- DAA - 插值搜索
- DAA - 跳转搜索
- DAA - 指数搜索
- DAA - 斐波那契搜索
- DAA - 子列表搜索
- DAA-哈希表
- 图论
- DAA-最短路径
- DAA - 多级图
- 最优成本二叉搜索树
- 堆算法
- DAA-二叉堆
- DAA-插入法
- DAA-Heapify 方法
- DAA-提取方法
- 复杂性理论
- 确定性计算与非确定性计算
- DAA-最大派系
- DAA - 顶点覆盖
- DAA - P 级和 NP 级
- DAA-库克定理
- NP 硬课程和 NP 完全课程
- DAA - 爬山算法
- DAA 有用资源
- DAA - 快速指南
- DAA - 有用的资源
- DAA - 讨论
设计与分析 - 插值搜索
插值搜索是二分搜索的改进变体。该搜索算法作用于所需值的探测位置。为了使该算法正常工作,数据收集应该是排序的形式并且均匀分布。
与线性搜索相比,二分搜索在时间复杂度上具有巨大的优势。线性搜索的最坏情况复杂度为 Ο(n),而二分搜索的最坏情况复杂度为 Ο(log n)。
在某些情况下,可以提前知道目标数据的位置。例如,在电话簿的情况下,如果我们要搜索“Morpheus”的电话号码。在这里,线性搜索甚至二分搜索都会显得很慢,因为我们可以直接跳转到存储以“M”开头的名称的内存空间。
二分查找中的定位
在二分搜索中,如果未找到所需的数据,则列表的其余部分将分为两部分:较低部分和较高部分。搜索在其中任何一个中进行。
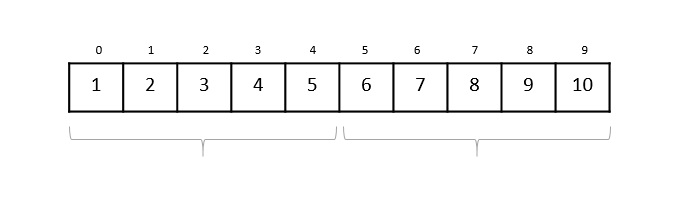
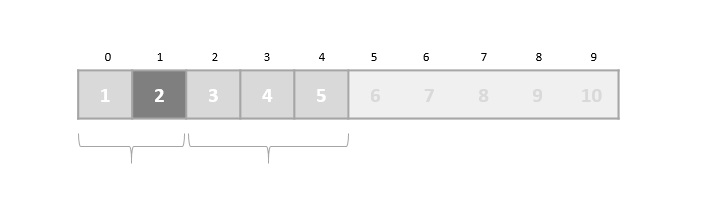
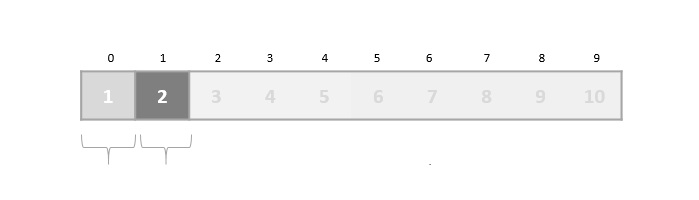
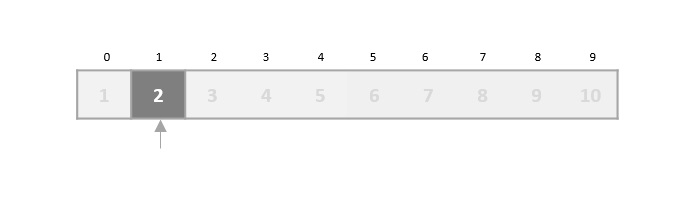
即使数据已排序,二分查找也无法探测所需数据的位置。
插补搜索中的位置探测
插值搜索通过计算探针位置来查找特定项目。最初,探测位置是集合中最中间项的位置。

如果发生匹配,则返回该项目的索引。要将列表分成两部分,我们使用以下方法 -
$$mid\, =\, Lo\, +\, \frac{\left ( Hi\, -\, Lo \right )\ast \left ( X\, -\, A\left [ Lo \right ] \右 )}{A\左 [ Hi \右 ]\, -\, A\左 [ Lo \右 ]}$$
其中 -
A = list Lo = Lowest index of the list Hi = Highest index of the list A[n] = Value stored at index n in the list
如果中间项大于该项,则在中间项右侧的子数组中再次计算探针位置。否则,将在中间项左侧的子数组中搜索该项。这个过程也在子数组上继续,直到子数组的大小减少到零。
插值搜索算法
由于它是现有 BST 算法的即兴改进,因此我们提到使用位置探测来搜索“目标”数据值索引的步骤 -
步骤 1 - 从列表中间开始搜索数据。
步骤 2 - 如果匹配,则返回该项目的索引,然后退出。
步骤 3 - 如果不匹配,则探测位置。
步骤 4 - 使用探测公式划分列表并找到新的中间项。
步骤 5 - 如果数据大于中间,则在更高的子列表中搜索。
步骤 6 - 如果数据小于中间,则在较低的子列表中搜索。
步骤 7 - 重复直到匹配。
伪代码
A → Array list
N → Size of A
X → Target Value
Procedure Interpolation_Search()
Set Lo → 0
Set Mid → -1
Set Hi → N-1
While X does not match
if Lo equals to Hi OR A[Lo] equals to A[Hi]
EXIT: Failure, Target not found
end if
Set Mid = Lo + ((Hi - Lo) / (A[Hi] - A[Lo])) * (X - A[Lo])
if A[Mid] = X
EXIT: Success, Target found at Mid
else
if A[Mid] < X
Set Lo to Mid+1
else if A[Mid] > X
Set Hi to Mid-1
end if
end if
End While
End Procedure
分析
在有利情况下,插值搜索算法的运行时间复杂度为Ο(log (log n)),而BST 的运行时间复杂度为Ο(log n) 。
例子
为了了解插值搜索中涉及的逐步过程,让我们看一个示例并解决它。
考虑下面给出的排序元素数组 -
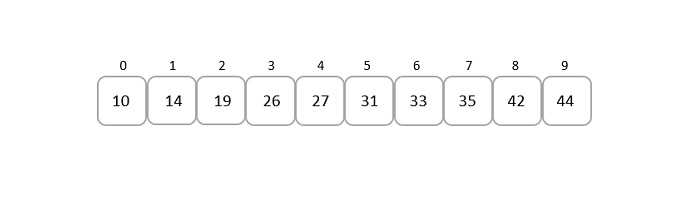
让我们搜索元素 19。
解决方案
与二分搜索不同,这种方法的中间点是使用以下公式选择的 -
$$mid\, =\, Lo\, +\, \frac{\left ( Hi\, -\, Lo \right )\ast \left ( X\, -\, A\left [ Lo \right ] \右 )}{A\左 [ Hi \右 ]\, -\, A\左 [ Lo \右 ]}$$
所以在这个给定的数组输入中,
Lo = 0, A[Lo] = 10 Hi = 9, A[Hi] = 44 X = 19
应用公式找到列表中的中间点,我们得到
$$mid\, =\, 0\, +\, \frac{\left ( 9\, -\, 0 \right )\ast \left ( 19\, -\, 10 \right )}{44\, -\, 10}$$
$$mid\, =\, \frac{9\ast 9}{34}$$
$$mid\, =\, \frac{81}{34}\,=\,2.38$$
由于mid是索引值,因此我们只考虑小数的整数部分。即,中值=2。
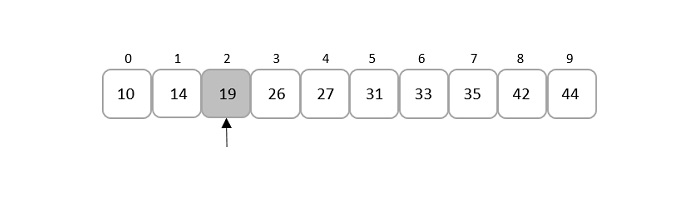
将给定的关键元素(即 19)与中间索引中存在的元素进行比较,发现两个元素都匹配。
因此,该元素位于索引 2 处。
例子
插值搜索是二分搜索的改进变体。该搜索算法作用于所需值的探测位置。为了使该算法正常工作,数据收集应该是排序且均匀分布的形式。
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAX 10
// array of items on which linear search will be conducted.
int list[MAX] = { 10, 14, 19, 26, 27, 31, 33, 35, 42, 44 };
int interpolation_search(int data){
int lo = 0;
int hi = MAX - 1;
int mid = -1;
int comparisons = 1;
int index = -1;
while(lo <= hi) {
printf("\nComparison %d \n" , comparisons ) ;
printf("lo : %d, list[%d] = %d\n", lo, lo, list[lo]);
printf("hi : %d, list[%d] = %d\n", hi, hi, list[hi]);
comparisons++;
// probe the mid point
mid = lo + (((double)(hi - lo) / (list[hi] - list[lo])) * (data - list[lo]));
printf("mid = %d\n",mid);
// data found
if(list[mid] == data) {
index = mid;
break;
} else {
if(list[mid] < data) {
// if data is larger, data is in upper half
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
// if data is smaller, data is in lower half
hi = mid - 1;
}
}
}
printf("\nTotal comparisons made: %d", --comparisons);
return index;
}
int main(){
//find location of 33
int location = interpolation_search(33);
// if element was found
if(location != -1)
printf("\nElement found at location: %d" ,(location+1));
else
printf("Element not found.");
return 0;
}
输出
Comparison 1 lo : 0, list[0] = 10 hi : 9, list[9] = 44 mid = 6 Total comparisons made: 1 Element found at location: 7
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 10
// array of items on which linear search will be conducted.
int list[MAX] = { 10, 14, 19, 26, 27, 31, 33, 35, 42, 44 };
int interpolation_search(int data){
int lo = 0;
int hi = MAX - 1;
int mid = -1;
int comparisons = 1;
int index = -1;
while(lo <= hi) {
cout << "\nComparison " << comparisons << endl;
cout << "lo : " << lo << " list[" << lo << "] = " << list[lo] << endl;
cout << "hi : " << hi << " list[" << hi << "] = " << list[hi] << endl;
comparisons++;
// probe the mid point
mid = lo + (((double)(hi - lo) / (list[hi] - list[lo])) * (data - list[lo]));
cout << "mid = " << mid;
// data found
if(list[mid] == data) {
index = mid;
break;
} else {
if(list[mid] < data) {
// if data is larger, data is in upper half
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
// if data is smaller, data is in lower half
hi = mid - 1;
}
}
}
cout << "\nTotal comparisons made: " << (--comparisons);
return index;
}
int main(){
//find location of 33
int location = interpolation_search(33);
// if element was found
if(location != -1)
cout << "\nElement found at location: " << (location+1);
else
cout << "Element not found.";
return 0;
}
输出
Comparison 1 lo : 0 list[0] = 10 hi : 9 list[9] = 44 mid = 6 Total comparisons made: 1 Element found at location: 7
import java.io.*;
public class InterpolationSearch {
static int interpolation_search(int data, int[] list) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = list.length - 1;
int mid = -1;
int comparisons = 1;
int index = -1;
while(lo <= hi) {
System.out.println("\nComparison " + comparisons);
System.out.println("lo : " + lo + " list[" + lo + "] = " + list[lo]);
System.out.println("hi : " + hi + " list[" + hi + "] = " + list[hi]);
comparisons++;
// probe the mid point
mid = lo + (((hi - lo) * (data - list[lo])) / (list[hi] - list[lo]));
System.out.println("mid = " + mid);
// data found
if(list[mid] == data) {
index = mid;
break;
} else {
if(list[mid] < data) {
// if data is larger, data is in upper half
lo = mid + 1;
} else {
// if data is smaller, data is in lower half
hi = mid - 1;
}
}
}
System.out.println("\nTotal comparisons made: " + (--comparisons));
return index;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int[] list = { 10, 14, 19, 26, 27, 31, 33, 35, 42, 44 };
//find location of 33
int location = interpolation_search(33, list);
// if element was found
if(location != -1)
System.out.println("\nElement found at location: " + (location+1));
else
System.out.println("Element not found.");
}
}
输出
Comparison 1 lo : 0 list[0] = 10 hi : 9 list[9] = 44 mid = 6 Total comparisons made: 1 Element found at location: 7
def interpolation_search( data, arr):
lo = 0
hi = len(arr) - 1
mid = -1
comparisons = 1
index = -1
while(lo <= hi):
print("\nComparison ", comparisons)
print("lo : ", lo)
print("list[", lo, "] = ")
print(arr[lo])
print("hi : ", hi)
print("list[", hi, "] = ")
print(arr[hi])
comparisons = comparisons + 1
#probe the mid point
mid = lo + (((hi - lo) * (data - arr[lo])) // (arr[hi] - arr[lo]))
print("mid = ", mid)
#data found
if(arr[mid] == data):
index = mid
break
else:
if(arr[mid] < data):
#if data is larger, data is in upper half
lo = mid + 1
else:
#if data is smaller, data is in lower half
hi = mid - 1
print("\nTotal comparisons made: ")
print(comparisons-1)
return index
arr = [10, 14, 19, 26, 27, 31, 33, 35, 42, 44]
#find location of 33
location = interpolation_search(33, arr)
#if element was found
if(location != -1):
print("\nElement found at location: ", (location+1))
else:
print("Element not found.")
输出
Comparison 1 lo : 0 list[ 0 ] = 10 hi : 9 list[ 9 ] = 44 mid = 6 Total comparisons made: 1 Element found at location: 7