
- 使用 Python 进行机器学习
- 家
- 基本
- Python生态系统
- 机器学习方法
- ML 项目的数据加载
- 通过统计了解数据
- 通过可视化了解数据
- 准备数据
- 数据特征选择
- 机器学习算法 - 分类
- 介绍
- 逻辑回归
- 支持向量机(SVM)
- 决策树
- 朴素贝叶斯
- 随机森林
- 机器学习算法 - 回归
- 随机森林
- 线性回归
- 机器学习算法 - 聚类
- 概述
- K均值算法
- 均值平移算法
- 层次聚类
- ML 算法 - KNN 算法
- 寻找最近的邻居
- 性能指标
- 自动工作流程
- 提高机器学习模型的性能
- 提高 ML 模型的性能(续……)
- 使用 Python 进行机器学习 - 资源
- 使用 Python 进行机器学习 - 快速指南
- 使用 Python 进行机器学习 - 资源
- 使用 Python 进行机器学习 - 讨论
聚类算法 - 均值平移算法
Mean-Shift 算法简介
如前所述,它是无监督学习中使用的另一种强大的聚类算法。与K-means聚类不同,它不做任何假设;因此它是一种非参数算法。
均值漂移算法基本上通过将点移向最高密度的数据点(即簇质心)来迭代地将数据点分配给簇。
K-Means 算法与 Mean-Shift 算法的区别在于,后者不需要提前指定簇的数量,因为簇的数量将由算法根据数据确定。
均值平移算法的工作原理
我们可以借助以下步骤了解 Mean-Shift 聚类算法的工作原理 -
步骤 1 - 首先,从分配给自己的集群的数据点开始。
步骤 2 - 接下来,该算法将计算质心。
步骤 3 - 在此步骤中,将更新新质心的位置。
步骤 4 - 现在,该过程将被迭代并移动到更高密度的区域。
步骤 5 - 最后,一旦质心到达无法进一步移动的位置,它将停止。
Python 中的实现
这是一个了解 Mean-Shift 算法如何工作的简单示例。在此示例中,我们将首先生成包含 4 个不同斑点的 2D 数据集,然后应用 Mean-Shift 算法来查看结果。
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
from sklearn.cluster import MeanShift
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import style
style.use("ggplot")
from sklearn.datasets.samples_generator import make_blobs
centers = [[3,3,3],[4,5,5],[3,10,10]]
X, _ = make_blobs(n_samples = 700, centers = centers, cluster_std = 0.5)
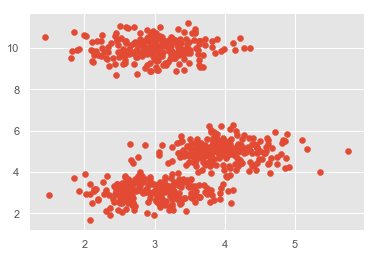
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1])
plt.show()
ms = MeanShift()
ms.fit(X)
labels = ms.labels_
cluster_centers = ms.cluster_centers_
print(cluster_centers)
n_clusters_ = len(np.unique(labels))
print("Estimated clusters:", n_clusters_)
colors = 10*['r.','g.','b.','c.','k.','y.','m.']
for i in range(len(X)):
plt.plot(X[i][0], X[i][1], colors[labels[i]], markersize = 3)
plt.scatter(cluster_centers[:,0],cluster_centers[:,1],
marker=".",color='k', s=20, linewidths = 5, zorder=10)
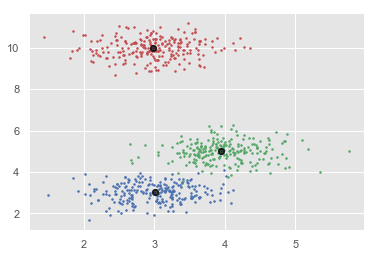
plt.show()
输出
[[ 2.98462798 9.9733794 10.02629344] [ 3.94758484 4.99122771 4.99349433] [ 3.00788996 3.03851268 2.99183033]] Estimated clusters: 3
的优点和缺点
优点
以下是 Mean-Shift 聚类算法的一些优点 -
它不需要像 K 均值或高斯混合那样进行任何模型假设。
它还可以对具有非凸形状的复杂簇进行建模。
它只需要一个参数,即带宽,它会自动确定集群的数量。
不存在像 K-means 那样的局部极小值问题。
不存在由异常值产生的问题。
缺点
以下是 Mean-Shift 聚类算法的一些缺点 -
均值漂移算法在高维情况下效果不佳,因为聚类数量突然变化。
我们对集群的数量没有任何直接控制,但在某些应用程序中,我们需要特定数量的集群。
它无法区分有意义和无意义的模式。