- Java RMI Tutorial
- Java RMI - Home
- Java RMI - Introduction
- Java RMI - RMI Application
- Java RMI - GUI Application
- Java RMI - Database Application
- Java RMI Useful Resources
- Java RMI - Quick Guide
- Java RMI - Useful Resources
- Java RMI - Discussion
Java RMI 应用程序
要编写 RMI Java 应用程序,您必须遵循以下步骤 -
- 定义远程接口
- 开发实现类(远程对象)
- 开发服务器程序
- 开发客户端程序
- 编译应用程序
- 执行应用程序
定义远程接口
远程接口提供特定远程对象的所有方法的描述。客户端与此远程接口进行通信。
创建远程接口 -
创建一个扩展属于该包的预定义接口Remote 的接口。
在此接口中声明客户端可以调用的所有业务方法。
由于远程调用时有可能出现网络问题,可能会出现名为RemoteException的异常;丢它。
以下是远程接口的示例。这里我们定义了一个名为Hello的接口,它有一个名为printMsg()的方法。
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
// Creating Remote interface for our application
public interface Hello extends Remote {
void printMsg() throws RemoteException;
}
开发实现类(远程对象)
我们需要实现在前面步骤中创建的远程接口。(我们可以单独写一个实现类,也可以直接让服务器程序实现这个接口。)
开发一个实现类 -
- 实现上一步中创建的接口。
- 提供远程接口的所有抽象方法的实现。
下面是一个实现类。在这里,我们创建了一个名为ImplExample的类,并实现了上一步中创建的Hello接口,并为此方法提供了打印消息的主体。
// Implementing the remote interface
public class ImplExample implements Hello {
// Implementing the interface method
public void printMsg() {
System.out.println("This is an example RMI program");
}
}
开发服务器程序
RMI服务器程序应该实现远程接口或扩展实现类。在这里,我们应该创建一个远程对象并将其绑定到RMIregistry。
开发服务器程序 -
创建一个要从其中调用远程对象的客户端类。
通过实例化实现类来创建远程对象,如下所示。
使用属于包java.rmi.server的UnicastRemoteObject类的方法exportObject()导出远程对象。
使用属于java.rmi.registry包的LocateRegistry类的getRegistry()方法获取 RMI 注册表。
使用名为Registry的类的bind()方法将创建的远程对象绑定到注册表。向此方法传递一个表示绑定名称和导出的对象的字符串作为参数。
以下是 RMI 服务器程序的示例。
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
public class Server extends ImplExample {
public Server() {}
public static void main(String args[]) {
try {
// Instantiating the implementation class
ImplExample obj = new ImplExample();
// Exporting the object of implementation class
// (here we are exporting the remote object to the stub)
Hello stub = (Hello) UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(obj, 0);
// Binding the remote object (stub) in the registry
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry();
registry.bind("Hello", stub);
System.err.println("Server ready");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Server exception: " + e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
开发客户端程序
在其中编写客户端程序,获取远程对象并使用该对象调用所需的方法。
开发客户端程序 -
从您打算调用远程对象的位置创建一个客户端类。
使用属于java.rmi.registry包的LocateRegistry类的getRegistry()方法获取 RMI 注册表。
使用属于包java.rmi.registry的Registry类的方法lookup()从注册表中获取对象。
对于此方法,您需要将表示绑定名称的字符串值作为参数传递。这将返回您远程对象。
Lookup() 返回一个 Remote 类型的对象,将其向下转换为 Hello 类型。
最后使用获得的远程对象调用所需的方法。
以下是 RMI 客户端程序的示例。
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
public class Client {
private Client() {}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// Getting the registry
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(null);
// Looking up the registry for the remote object
Hello stub = (Hello) registry.lookup("Hello");
// Calling the remote method using the obtained object
stub.printMsg();
// System.out.println("Remote method invoked");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Client exception: " + e.toString());
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
编译应用程序
编译应用程序 -
- 编译远程接口。
- 编译实现类。
- 编译服务器程序。
- 编译客户端程序。
或者,
打开存储所有程序的文件夹并编译所有 Java 文件,如下所示。
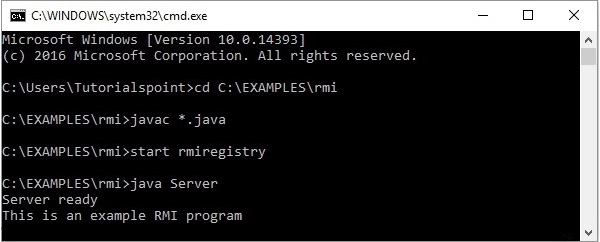
Javac *.java
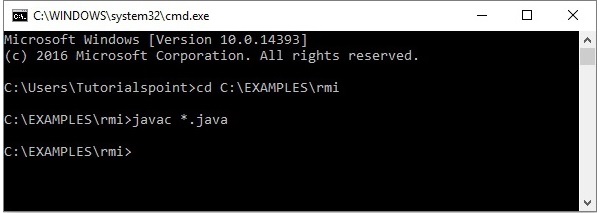
执行应用程序
步骤 1 -使用以下命令启动rmi注册表。
start rmiregistry
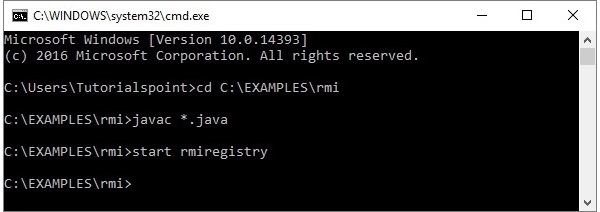
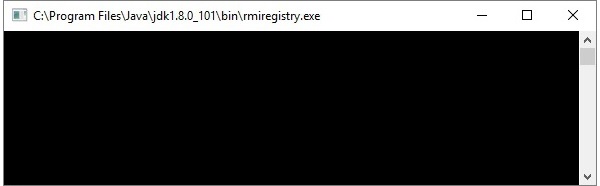
这将在单独的窗口上启动rmi注册表,如下所示。
步骤 2 - 运行服务器类文件,如下所示。
Java Server
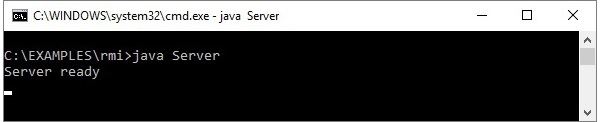
步骤 3 - 运行客户端类文件,如下所示。
java Client
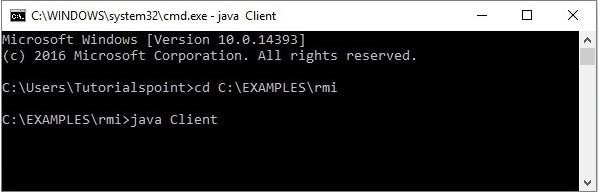
验证- 一旦启动客户端,您就会在服务器中看到以下输出。