
- JasmineJS 教程
- JasmineJS - 主页
- JasmineJS - 概述
- JasmineJS - 环境设置
- JasmineJS - 编写文本和执行
- JasmineJS - BDD 架构
- JasmineJS - 测试构建块
- JasmineJS - 匹配器
- JasmineJS - 跳过块
- JasmineJS - 平等检查
- JasmineJS - 布尔检查
- JasmineJS - 顺序检查
- JasmineJS - 空检查
- JasmineJS - 不平等检查
- JasmineJS - 不是数字检查
- JasmineJS - 异常检查
- JasmineJS - beforeEach()
- JasmineJS - afterEach()
- JasmineJS - 间谍
- JasmineJS 有用资源
- JasmineJS - 快速指南
- JasmineJS - 有用的资源
- JasmineJS - 讨论
JasmineJS - 测试构建块
在本章中,我们将讨论 Jasmine 测试的构建块。
套房楼
Jasmine 是一个 JavaScript 测试框架。Suite是 Jasmine 框架的基本构建块。为特定文件或函数编写的类似类型测试用例的集合称为一套。它包含另外两个块,一个是“Describe()”,另一个是“It()”。
一个 Suite 块只能有两个参数,一个是“该套件的名称”,另一个是实际调用要测试的单元功能的“函数声明” 。
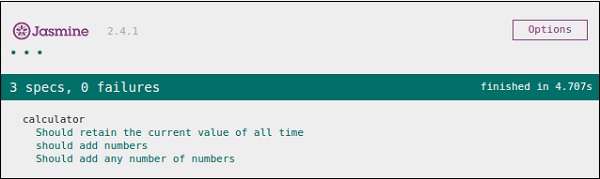
在下面的示例中,我们将创建一个套件,对add.js文件中的 add 函数进行单元测试。在这个例子中,我们有一个名为“calculator.js”的JS文件,它将通过Jasmine进行测试,对应的Jasmine规范文件是“CalCulatorSpec.js”。
计算器.js
window.Calculator = {
currentVal:0,
varAfterEachExmaple:0,
add:function (num1) {
this.currentVal += num1;
return this.currentVal;
},
addAny:function () {
var sum = this.currentVal;
for(var i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
sum += arguments[i];
}
this.currentVal = sum;
Return this.currentVal;
},
};
CalCulatorSpec.js
describe("calculator",function() {
//test case: 1
it("Should retain the current value of all time", function () {
expect(Calculator.currentVal).toBeDefined();
expect(Calculator.currentVal).toEqual(0);
});
//test case: 2
it("should add numbers",function() {
expect(Calculator.add(5)).toEqual(5);
expect(Calculator.add(5)).toEqual(10);
});
//test case :3
it("Should add any number of numbers",function () {
expect(Calculator.addAny(1,2,3)).toEqual(6);
});
});
在上面的函数中,我们声明了两个函数。函数add将添加作为该函数参数给出的两个数字,另一个函数addAny应该添加作为参数给出的任何数字。
创建该文件后,我们需要将该文件添加到head 部分的“SpecRunner.html”中。成功编译后,将生成以下输出。
嵌套套房街区
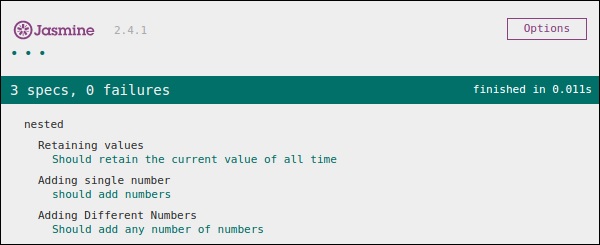
套房块可以在另一个套房块内包含许多套房块。以下示例将向您展示如何在另一个套件块中创建不同的套件块。我们将创建两个 JavaScript 文件,一个名为“NestedSpec.js”,另一个名为“nested.js”。
嵌套规范.js
describe("nested",function() {
// Starting of first suite block
// First block
describe("Retaining values ",function () {
//test case:1
it ("Should retain the current value of all time", function () {
expect(nested.currentVal).toBeDefined();
expect(nested.currentVal).toEqual(0);
});
}); //end of the suite block
//second suite block
describe("Adding single number ",function () {
//test case:2
it("should add numbers",function() {
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(5);
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(10);
});
}); //end of the suite block
//third suite block
describe("Adding Different Numbers",function () {
//test case:3
it("Should add any number of numbers",function() {
expect(nested.addAny(1,2,3)).toEqual(6);
});
}); //end of the suite block
});
嵌套.js
window.nested = {
currentVal: 0,
add:function (num1) {
this.currentVal += num1;
return this.currentVal;
},
addAny:function () {
Var sum = this.currentVal;
for(var i = 0;i < arguments.length; i++) {
sum += arguments[i];
}
this.currentVal = sum;
return this.currentVal;
}
};
在 head 部分添加该文件后,运行specRunner.html文件,上面的代码将生成以下输出。
描述块
正如前面所讨论的,描述块是套件块的一部分。与 Suite 块一样,它包含两个参数,一个是“描述块的名称”,另一个是“函数声明”。在接下来的示例中,我们将通过许多描述块来了解 Jasmine 套件块的工作流程。以下是完整描述块的示例。
describe("Adding single number ",function () {
it("should add numbers",function() {
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(5);
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(10);
});
}
IT区块
与描述块一样,我们也介绍了 IT 块。它位于描述块内。这是实际包含每个单元测试用例的块。在下面的代码中,一个描述块内有一些IT块。
describe("Adding single number ",function () {
// test case : 1
it("should add numbers",function() {
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(5);
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(10);
});
//test case : 2
it("should add numbers",function() {
expect(nested.addAny(1,2,3)).toEqual(6);
});
}
预期区块
Jasmine Expect允许您从所需的函数或 JavaScript 文件中编写您的期望。它属于IT块。一个 IT 块可以有多个 Expect 块。
以下是 Expect 块的示例。此 Expect 块提供了多种方法来对 JavaScript 函数或 JavaScript 文件进行单元测试。每个 Expect 块也称为匹配器。有两种不同类型的匹配器,一种是内置匹配器,另一种是用户定义的匹配器。
describe("Adding single number ",function () {
// test case : 1
it("should add numbers",function() {
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(5);
expect(nested.add(5)).toEqual(10);
});
//test case : 2
it("should add numbers",function() {
expect(nested.addAny(1,2,3)).toEqual(6);
});
}
在接下来的章节中,我们将讨论 Expect 块的不同内置方法的各种用法。