- FastAPI教程
- FastAPI - 主页
- FastAPI - 简介
- FastAPI - 你好世界
- FastAPI-开放API
- FastAPI - Uvicorn
- FastAPI - 类型提示
- FastAPI - IDE 支持
- FastAPI - 休息架构
- FastAPI - 路径参数
- FastAPI - 查询参数
- FastAPI - 参数验证
- FastAPI - Pydantic
- FastAPI - 请求正文
- FastAPI - 模板
- FastAPI - 静态文件
- FastAPI - HTML 表单模板
- FastAPI - 访问表单数据
- FastAPI - 上传文件
- FastAPI - Cookie 参数
- FastAPI - 标头参数
- FastAPI - 响应模型
- FastAPI - 嵌套模型
- FastAPI - 依赖关系
- FastAPI - CORS
- FastAPI - Crud 操作
- FastAPI - SQL 数据库
- FastAPI - 使用 MongoDB
- FastAPI - 使用 GraphQL
- FastAPI - Websocket
- FastAPI - FastAPI 事件处理程序
- FastAPI - 安装子应用程序
- FastAPI - 中间件
- FastAPI - 安装 Flask 应用程序
- FastAPI - 部署
- FastAPI 有用资源
- FastAPI - 快速指南
- FastAPI - 有用的资源
- FastAPI - 讨论
FastAPI - 静态文件
通常需要在模板响应中包含一些即使存在某些动态数据也保持不变的资源。此类资源称为静态资产。媒体文件(.png、.jpg 等)、用于执行某些前端代码的 JavaScript 文件或用于格式化 HTML(.CSS 文件)的样式表都是静态文件的示例。
为了处理静态文件,您需要一个名为aiofiles的库
pip3 install aiofiles
接下来,从fastapi.staticfiles模块导入StaticFiles类。它的对象是 FastAPI 应用程序对象的mount()方法的参数之一,用于在当前应用程序文件夹中分配“static”子文件夹来存储和提供应用程序的所有静态资源。
app.mount(app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static")
例子
在以下示例中,FastAPI 徽标将在 hello.html 模板中呈现。因此,“fa-logo.png”文件首先放置在静态文件夹中。现在可以在 HTML 代码中用作<img>标记的src属性。
from fastapi import FastAPI, Request
from fastapi.responses import HTMLResponse
from fastapi.templating import Jinja2Templates
from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
app = FastAPI()
templates = Jinja2Templates(directory="templates")
app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory="static"), name="static")
@app.get("/hello/{name}", response_class=HTMLResponse)
async def hello(request: Request, name:str):
return templates.TemplateResponse("hello.html", {"request": request, "name":name})
\templates\hello.html的 HTML 代码如下 -
<html>
<body>
<h2>Hello {{name}} Welcome to FastAPI</h2>
<img src="{{ url_for('static', path='fa-logo.png') }}" alt="" width="300">
</body>
</html>
</pre>
运行 Uvicorn 服务器并访问 URL:http://localhost/hello/Vijay。徽标出现在浏览器窗口中,如图所示。

例子
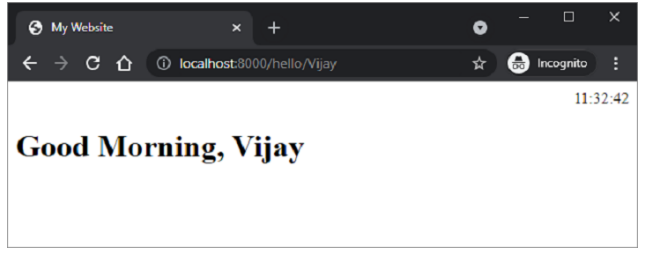
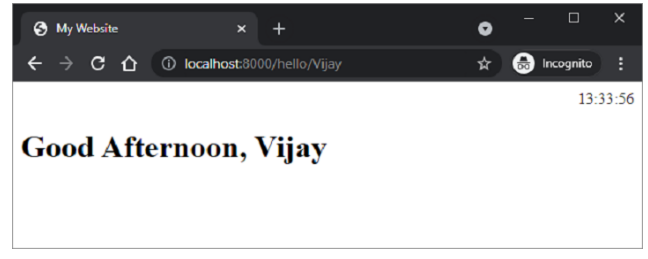
这是静态文件的另一个示例。JavaScript 代码 hello.js 包含要在以下 HTML 脚本 (\templates\hello.html) 中的onload事件上执行的myfunction()的定义
<html>
<head>
<title>My Website</title>
<script src="{{ url_for('static', path='hello.js') }}"></script>
</head>
<body onload="myFunction()">
<div id="time" style="text-align:right; width="100%"></div>
<h1><div id="ttl">{{ name }}</div></h1>
</body>
</html>
hello.js代码如下 - ( \static\hello.js)
function myFunction() {
var today = new Date();
var h = today.getHours();
var m = today.getMinutes();
var s = today.getSeconds();
var msg="";
if (h<12) {
msg="Good Morning, ";
}
if (h>=12 && h<18) {
msg="Good Afternoon, ";
}
if (h>=18) {
msg="Good Evening, ";
}
var x=document.getElementById('ttl').innerHTML;
document.getElementById('ttl').innerHTML = msg+x;
document.getElementById('time').innerHTML = h + ":" + m + ":" + s;
}
该函数检测当前时间的值,并根据一天中的时间为msg变量分配适当的值(早上好、下午好或晚上好)。
保存/static/hello.js,修改\templates\hello.html并重新启动服务器。浏览器应显示当前时间及其下方相应的消息。